Topic: Bipolar Disorder
Author: Aya M. Al-Kailani
Scientific Editor: Ahda Jbarah
Linguistic Editor: Hala Qaryouti
Overview
Bipolar disorder (BPD), also known as manic-depressive illness (MDI), is a mental disorder consisting of abnormally extreme alterations in mood, concentration, and activity levels. These shifts in mood include emotional highs (mania or hypomania) and lows (depression). This disorder is a serious lifelong challenge faced by many people in the world[1]. The National Institute of Mental Health estimates that bipolar disorder affects approximately 5.7 million adult Americans, or about 2.6% of the U.S. population age 18 and older every year.
There are multiple types of bipolar and related disorders including mania/ hypomania and depression. The main divisions of bipolar disorder are Bipolar I, Bipolar II, cyclothymic disorder, and other disorders. These different diagnoses depend on the type and severity of symptoms present in each patient.
Prevalence
The global prevalence for BPD ranged from 0.4% to 1.6% between the mid-1970s and 2000. By the late 1990s to the 2000s, the prevalence had climbed from approximately 5% to 7% [2]. The lifelong prevalence of bipolar disorder ranges from 0.9% to 2.1% in the United States[3]. Studies also show differences in the lifetime prevalence of each of the different types of bipolar disorder. For bipolar disorder type I (BPI), the lifetime prevalence is (1.0%), while for bipolar disorder type II (BPII) it is (1.1%). For subthreshold bipolar disorders, prevalence is between (2.4–4.7%) [4].
For both BPI and BPII, the age of onset varies greatly, ranging from childhood to 50 years, with a mean of approximately 21 years. It is important to mention that patients diagnosed with recurrent major depression may actually have bipolar disorder but develop their first manic episode over the age of 50 years, as a part of the disease progression. However, the onset of mania in patients older than 50 years should be investigated for a possible medical or neurological disorder as well.
Most studies have concluded an almost equal male-to-female ratio in the prevalence of BPD. However, studies also report an increased risk in women for some types of bipolar disorder, such as BPII and rapid-cycling bipolar disorder[5].
Pathophysiology
The exact pathophysiology of bipolar disorder has not been determined, but studies show a strong genetic association. According to Edvardsen et. al, first-degree relatives of a person with bipolar disorder are approximately 7 times more likely to develop bipolar disorder than the rest of the population [6]. However, the genetic component of BPD appears to be complex due to the contribution of multiple different genetic alleles. Bipolar disorder inheritance has been associated with several genes including multiple genes in the MAFD loci [7-15], the CACNA1C gene[16], and the ANK3 gene[16]. Many studies suggest that certain large genetic deletions and duplications are associated with mental illnesses, with both bipolar disorder and schizophrenia being the most commonly associated illnesses [17].
Myelin, the sheath covering axons, allows efficient conduction of nerve impulses in the nervous system. Its loss is thought to play a role in neurological diseases and mental illnesses, one of which is bipolar disorder. Abnormal myelination in several brain regions has been seen in imaging studies of persons with bipolar disorder. This feature has been useful when comparing patients who have certain genetic components with those who have bipolar disorder and these imaging findings. [18.19]
Risk Factors
Certain factors increase the likelihood of developing bipolar disorder, and trigger the first episode in those with an already existing tendency to develop BPD. Those risk factors include:
- Stressful or traumatic events, such as the death of a loved one
- Having a first-degree relative (parents or siblings) with bipolar disorder
- Drug or alcohol abuse
According to 2119 studies, the risk factors for developing bipolar disorder can be grouped in 3 main categories:
- Neurodevelopmental risk factors (e.g. maternal influenza during pregnancy)
- Substance abuse (e.g.: cocaine, cannabis, opioids, tranquilizers, stimulants, sedatives)
- Physical/psychological stress (parental loss, adversities, abuse, brain injury). [21]
Clinical Presentation
Mood disorders in general (BPD and depressive disorders) are characterized by mood episodes; a combination of symptoms comprising a predominant mood state in distinct periods of time. Types of mood episodes seen in BPD include major depressive, manic, and hypomanic episodes (depending on the type of BPD diagnosed).
- Mania and Hypomania
Mania and hypomania are two different features with similar symptoms, as according to DSM-5 (Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, fifth edition), to diagnose the former or the latter, three or more of the following criteria must be present:
- Grandiosity
- Decreased need for sleep
- Excessive talking or pressured speech
- Racing thoughts or flight of ideas
- Distractibility
- Increase in goal-focused activity at home/ work, or sexually
- Excessive pleasurable activities, often with painful consequences
However, the difference between mania and hypomania is highlighted through the following:
- Manic episodes include at least 1 week of profound mood disturbance, characterized by gateway criteria (elation, expansiveness or irritability) and at least 3 of the symptoms mentioned prior[20]. On the other hand, hypomanic episodes are characterized by at least 4 consecutive days of three or more of the symptoms above.
- Mania is more severe and causes significant dysfunction in the social setting, as well as relationship hurdles whereas hypomania is not severe enough to cause social impairment or dysfunction.
- Mania can trigger psychosis episodes (a break from reality) while hypomania doesn’t.
- Manic symptoms are usually severe enough to require hospitalization, while hypomanic symptoms do not require hospital admission.
- Depression
Major depressive episodes (MDE) are a part of the mood shifts that occur in Bipolar Disorder. According to DSM-5, in an MDE, the patient experiences 5 or more of the following symptoms over a continuous period of 2 weeks, with at least 1 of which being criterion A or B: [20]
- Depressed mood
- Marked decrease in pleasure or interest in nearly all activities
- Significant change in appetite or weight
- Hypersomnia or insomnia
- Psychomotor retardation or agitation
- Loss of energy or fatigue
- Feelings of worthlessness or excessive guilt
- Decreased concentration ability or marked indecisiveness
- Preoccupation with death or suicide, or having suicidal plans/ attempts
DSM -5 Diagnostic Criteria[22]
According to the DSM-5, to diagnose bipolar I disorder, the occurrence of a manic episode is a must. This may be preceded or followed by hypomanic episode or MDE:
- period of an abnormal persistent increase in energy or irritability for at least 1 week, present most of the day almost every day (any duration if hospitalization is necessary).
- During this period, at least 3 of the aforementioned symptoms of manic/hypomanic episodes (4 if there is only mood irritability) are present and represent a significant change from the individual’s usual behavior.
- A mood disturbance severe enough to cause marked impairment in functioning or to necessitate hospital admission to prevent harmful behavior and/or due to psychotic features.
- The episode is not caused by physiological effects of a substance (e.g., drug abuse, a medication, or other treatment) or another medical condition.
Bipolar II Disorder diagnosis necessitates meeting criteria for a current/ past hypomanic episode as well as those for a current or past MDE:
- A distinct period of hypomania (mood disturbance and increased energy and activity) lasting at least 4 consecutive days most of the day nearly daily
- During this period, 3 or more of the aforementioned symptoms of manic/ hypomanic episodes (4 if there is only mood irritability) have persisted to cause noticeable change from individual’s baseline behavior
- The episode is associated with an unmistakable change in functioning different from the individual’s behavior when asymptomatic.
- The mood disturbance and change in functioning are noticed by others.
- The episode does not lead to marked occupational functioning nor necessitates hospital admission.
- The episode is not caused by physiological effects of substance abuse.
- Must meet criteria of at least one hypomanic episode and at least one MDE
- There has never been a manic episode
- The occurrence of the hypomanic episode(s) and MDE(s) can not be better explained by schizophrenia spectrum disorders or other psychotic disorders.
- The symptoms of depression or the unpredictability caused by frequent changes between depression and hypomania causes distress or impairment in several important areas of functioning.
Cyclothymic disorder is diagnosed when an adult experiences mood cycling over a consecutive period of two years without meeting the diagnostic criteria for bipolar I, bipolar II, or depressive disorders. In children and adolescents, diagnosis requires only one year of hypomanic and depressive periods.
According to DSM-5, patients must experience the following symptoms for diagnosis of cyclothymic disorder:
- Multiple periods of hypomanic symptoms for at least two years that do not meet the criteria for hypomanic episodes.
- Multiple periods of depressive symptoms that do not meet criteria for an MDE.
- The person has experienced the cycling periods mentioned above for at least half the time, and has not been free of symptoms for more than two months.
- The symptoms experienced are not caused by another psychological condition.
- The symptoms are not due to an organic cause.
- The symptoms impair the person’s ability to socialize, work, or function in different aspects of life.
Treatment
Bipolar disorder is a lifelong illness with alternating episodes of mania and depression that typically recur. Between these episodes, many patients experience a symptom-free period. BPD patients should be always evaluated for a possible manic, hypomanic, or mixed episode, and those with bipolar depression should be evaluated for suicidality, acute or chronic psychosis, or other unstable or dangerous conditions [23].
Continuous, long-term treatment can help manage BPD symptoms. There is a wide variety of different available treatments (e.g.: medications, psychotherapy, electroconvulsive therapy, transcranial magnetic stimulation, and healthy lifestyle implementations). Hospitalization may be needed if the patient behaves dangerously, feels suicidal or acquires a psychotic behavior. Hospital stays can help calm the patients and stabilize their mood, whether during a manic or a major depressive episode.
- Pharmacologic Therapy
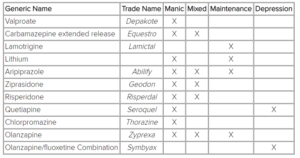
The pharmacological treatment of choice depends on the episode that the patient is experiencing, and the symptoms that are present. There are several drugs indicated for acute manic episodes. These drugs mainly consist of antipsychotic agents, valproate, and benzodiazepines (lorazepam, clonazepam). The following table includes the FDA-approved drugs for bipolar disorder, depending on the type of episode.
- Psychotherapy
Psychotherapy is a very important constituent of bipolar disorder treatment. Several types of psychotherapy can be provided, including:
- Interpersonal and social rhythm therapy (IPSRT) which focuses on establishing a healthy daily routine in patients’ lives,
- Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) focuses on replacing unwanted behavior with positive behavior,
- Family-focused therapy helps the patient’s loved ones recognize the patient’s mood swings and provides them with better understanding of how to manage the condition.
- Electroconvulsive therapy
ECT is the oldest among the treatments introduced in the psychiatric field, and the only one still in use to this day as it remains a treatment option for many mental illnesses. ECT is a generally safe procedure done under general anesthesia where small electrical currents are passed through the patient’s brain to provide relief and quickly improve symptoms of certain mental disorders. Changes are often observed within 1 week of therapy, which is faster than pharmaceutical treatments.
Electroconvulsive therapy is indicated in BPD when:
- rapid treatment is needed
- the risks of ECT are less than that of other treatments
- bipolar disorder is refractory to other treatment methods.
A study revealed that 313 of 400 patients with acute mania who received ECT showed significant clinical improvement. [24]
- Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation
Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) is a new approach to brain stimulation. It involves delivering magnetic waves to an awake patient most days for one month. Research has shown that TMS has a role in fighting different types of depression. Nonetheless, its role in the treatment of bipolar disorder is still under observation, but provides a promising approach for treating patients who have failed to respond to other methods of treatment. [25]
- Diet and Exercise
Healthy habits including regular exercise have a role in alleviating many symptoms experienced in mental illnesses, including bipolar disorder. Patients with bipolar disorder usually have a sedentary lifestyle due to their condition, which contributes to developing other medical diseases. Aerobic exercise in particular may be beneficial for both their mental and physical health.[26]
Patients experiencing a depressive episode are encouraged to exercise, develop a regular schedule of their daily activities, and a regular sleep schedule. Both exercise and regular schedule are primary to surviving this lifelong illness.
Prognosis
To conclude, the prognosis of bipolar disorder depends on the individual course of each patient’s illness. Comorbidities and psychotic symptoms associated with bipolar disorder have a negative influence on the prognosis of this mental disorder.[27]
If left untreated, bipolar disorder can result in serious complications including drug and alcohol abuse, suicidal attempts, legal and financial problems, damaged relationships, and poor social functioning. It is therefore very critical to appropriately diagnose, follow-up, and provide these patients with the correct treatment regimens that help them in the best way possible. Bipolar disorder is a lifelong illness that can be manageable if the correct approach is taken.